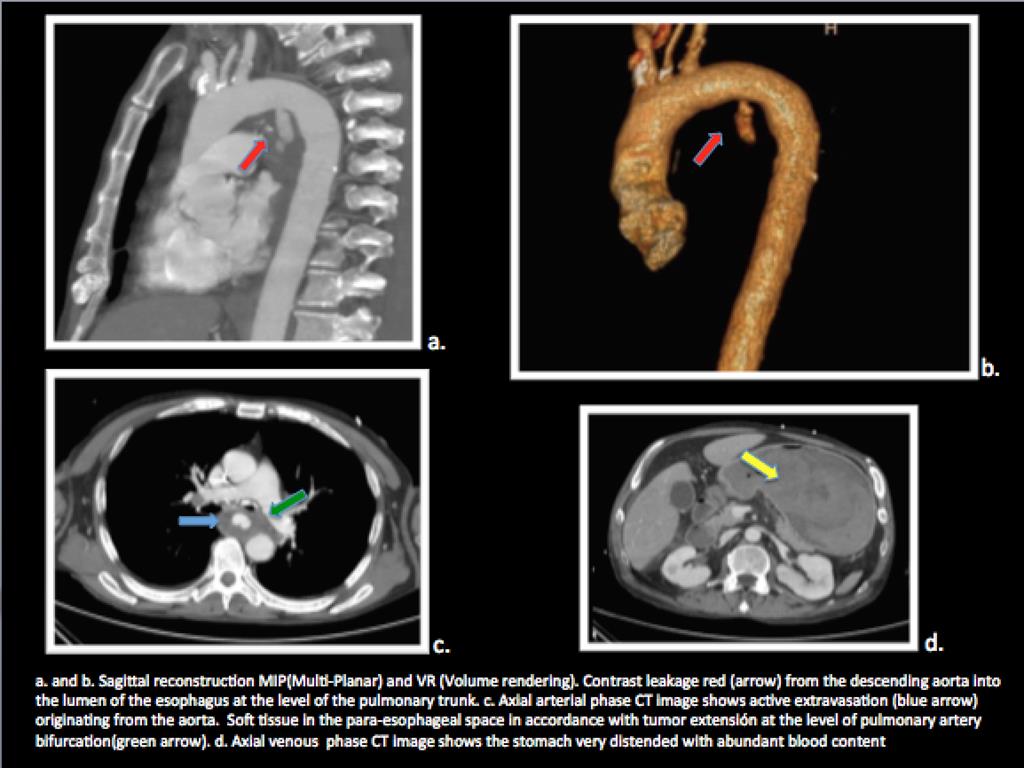
Hospital: Hospital Universitario de 12 Octubre.
Nº: C2019-245
Aut@r o Autores: G. García Galarraga, C. Cruz Conde, L. Ibáñez Sanz, E. Martínez Chamorro, N. Pérez Peláez, S. Alonso Charterina.
Presentación
A 54-year-old male with a history of Barrett's esophagus, who presented with high digestive hemorrhage and hemodynamic instability. Endoscopy is performed, observing a stenotic lesion in the proximal esophagus with a malignant appearance that does not allow the endoscope to pass. In the face of a new episode of instability and bleeding, CT angiography was decided, in which the following findings are observed: Mass in the middle third of the esophagus that contacts the lower portion of the aortic arch and the carina. Contrast leakage from the aortic arch into the lumen of the mass. Stomach very distended with abundant blood content. These findings suggested an aortoesophageal fistula (AEF) secondary to an esophageal tumor. Given the findings of large esophageal tumor with very extensive infiltration the patient is considered inoperable. Supportive treatment is decided. The patient died a few hours later.
Discusión
We present this case due to the clinical severity and urgency of pathology as rare as AEF. CT angiography is a very useful tool in the diagnosis of any upper gastrointestinal bleeding, as an alternative to failed or nondiagnostic endoscopy, due to its high availability and spatial resolution, being able to diagnose not only this entity but also to give us information about its exact location and cause for possible treatment. The most frequent causes of AEF are primary aortic or esophageal: Aneurysm of the thoracic aorta (52%), foreign body ingestion, primary esophageal cancer, and aortic dissection. Secondary causes are infrequent but are increasing due to the use of esophageal endoprosthesis in the esophageal cancer. Conventional treatment consists of thoracotomy and replacement or exclusion of the affected aortic segment through the interposition of a prosthesis. Depending on the cause, esophageal surgery may be necessary (cervical esophagostomy ...) Endovascular repair is an alternative that presents lower morbidity and mortality associated with the procedure.
Conclusión
The AOF is an urgent and serious pathology, requiring CT angiography for a rapid and accurate diagnosis. Being able to determine the cause and the exact place.
Bibliografía
- Hollander J E, Quick G. Aortoesophageal fistula: a comprehensive review of the literature. Am J Med 1991, 91: 279-87. - Bergoeing RM, Mertens MR, Mariné ML, Valdés EF, Kramer SchA, Nervi NB et al. Endovascular treatment of aorto-esophage