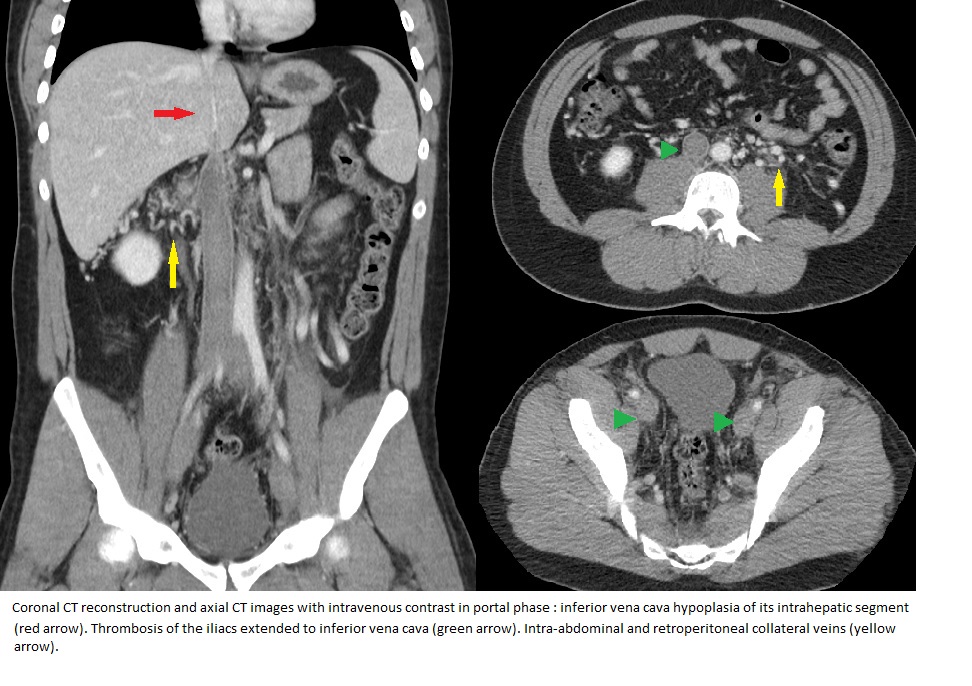
Hospital: Hospital Universitario de Canarias.
Nº: C2019-721
Aut@r o Autores: M.M. Sanchez, D. Martin Rodriguez, X. Plasencia Cruz, A. Rodriguez Fuentes, M. Fuentes García.
Presentación
A 27-year-old male with lower back pain irradiated to both extremities as well as increased perimeter of the lower left limb. No personal history of interest. Blood test: D-dimer of 7515. Ultrasound: bilateral femoro-iliac deep venous thrombosis extending to the inferior vena cava (IVC). CT: Filiform appearance of the intrahepatic IVC. Prominent acigos and lumbar veins. Increased perirenal and retroperitoneal collateral circulation. Lumbar plexus ingurgitation. Bilateral femoro-iliac deep venous thrombosis extended to IVC and right renal vein.
Discusión
The prevalence of IVC agenesis is 0.005-1% in the general population. It is usually segmental being the retrohepatic segment the most commonly affected. It may be asymptomatic or present at an early age with symptoms such as: venous insufficiency in the lower limbs, frequently bilateral idiopathic depth venous thrombosis (DVT), and pelvic congestion syndrome with lower back pain (both present in our case) and varicocele. In patients younger than 30 years with bilateral DVT, the prevalence of this vascular malformation increases to 5-6.7%. Contrast-enhanced CT is the technique of choice in DVT if it is bilateral or affects proximal veins. This technique is able to demonstrate abnormalities of the IVC and rules out the presence of pelvic masses that may obstruct venous flow (first diagnosis of presumption in our case). Clinical management consists of life-long anticoagulation.
Conclusión
Agenesis or hypoplasia of the IVC constitute a rare entity and are associated with deep vein thrombosis, especially in patients younger than 30 years with bilateral DVT.
Bibliografía
- Bass JE, Redwine MD, Kramer LA, Huynh PT, Harris JH Jr. Spectrum of congenital anomalies of the inferior vena cava: cross-sectional imaging findings. RadioGraphics 2000,20:639-652 - Tienda Flores S M.J., Awad F., Aguilar J.J., Gonzalez R., Iribarren M.